Rabin-Karp Fingerprint
Rabin-Karp fingerprint(RK) 基于 modular hashing:
- Compute a hash of pattern characters
0toM - 1. - For each
i, compute a hash of text charactersitoM + i - 1. - If pattern hash = text substring hash, check for a match.
如果在一一比较中对text的每个子串都重新计算hash,那么速度比暴力算法还慢。
所以算法的关键在于如何高效地计算哈希值:Horner’s method - M阶多项式hash的线性时间方法
$$a^b \pmod c = (a \pmod c)^b$$引理:
$$(a \times b) \pmod c = [( a \pmod c ) \times (b \pmod c) ] \pmod c$$即积的取余等于取余的积的取余.
具体证明可参考位操作 - 快速幂/快速幂取余
根据modulars算术的基本性质,在每个算术运算后除以$Q$取余数,和执行完所有算术运算后再取除以Q的余数的结果一样。比如加法 $a+b = c$, then $a\pmod N+b\pmod N \equiv c$. 其中$\equiv$表示Congruence, 即$15 \equiv -9\pmod{12}$表示$15$和$9$对$12$取余的余数相同. 同理
- If $a\equiv b\pmod N$, then $a+k \equiv b+k \pmod N$ for any integer $k$.
- If $a\equiv b\pmod N$, and $c\equiv d\pmod N$, then $a+c \equiv b+d \pmod N$.
- If $a \equiv b\pmod N$, then $-a \equiv -b\pmod N$.
乘法运算的取余满足:
- If $a \cdot b = c$, then $a\pmod N\cdot b\pmod N \equiv c \pmod{N}$.
- If $a \equiv b \pmod{N}$, then $ka \equiv kb \pmod{N}$ for any integer $k$.
- If $a \equiv b \pmod{N}$ and $c \equiv d \pmod{N}$, then $ac \equiv bd \pmod{N}$.
Exponentiation:
- If $a\equiv b\pmod{N}$, then $a^k \equiv b^k \pmod{N}$ for any positive integer kk.
使用多项式 Hash 计算pattern的hash,$h(d) = \Sigma d_i \times b^i \pmod Q$:
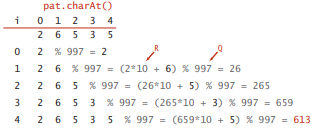
// Compute hash for M-digit key
private long hash(String key, int M)
{
long h = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++)
h = (R * h + key.charAt(j)) % Q;
return h;
}
RK算法的核心是,在pattern和text的对比中,如何动态地利用前面位置i已计算的值来计算新位置i+1的哈希. 给定$x_i$,如何计算$x_{i+1}$:
其中M-digit, base-R integer, modulo Q
$$x_{i+1} = t_{i+1}R^{M-1} + T_{i+2}R^{M-2} + ... + t_{i+M}R^0$$$$x_{i+1} = (x_i - t_i R^{M-1}) R + t_{i+M}$$根据这个关系可知, 我们不必动态维护$x_i$值,而只需维护其除$Q$的余数即可。而且,$R^{M-1}$是可以预先计算的.

同时为了避免出现负数, 需要在每次运算中加一次Q(不影响取余结果)
$$\begin{equation} \begin{aligned} (x_i + 1) \pmod Q &= (x_i + Q - t_i \times RM) \pmod Q \\ &= (x_i - t_i \times RM) \pmod Q + (t_i \times Q) \pmod Q \end{aligned} \end{equation} $$于是得出具体的搜索方法
public class RabinKarp
{
private String pat; // pattern (only needed for Las Vegas)
private long patHash; // pattern hash value
private int M; // pattern length
private long Q; // a large prime
private int R = 256; // alphabet size
private long RM; // R^(M-1) % Q
public RabinKarp(String pat)
{
this.pat = pat; // save pattern (only needed for Las Vegas)
this.M = pat.length();
Q = longRandomPrime(); // See Exercise 5.3.33.
RM = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= M-1; i++) // Compute R^(M-1) % Q for use
RM = (R * RM) % Q; // in removing leading digit.
patHash = hash(pat, M);
}
/** check for hash collision using rolling hash function */
public int search(String txt)
{ // Search for hash match in text.
int N = txt.length();
long txtHash = hash(txt, M);
if (patHash == txtHash) return 0; // Match at beginning.
for (int i = M; i < N; i++)
{ // Remove leading digit, add trailing digit, check for match.
txtHash = (txtHash + Q - RM*txt.charAt(i-M) % Q) % Q;
txtHash = (txtHash*R + txt.charAt(i)) % Q;
if (patHash == txtHash)
if (check(i - M + 1)) return i - M + 1; // match
}
return N; // no match found
}
}

Monte Carlo Correctness
存在哈希冲突, 如果要保证100%的字符匹配准确, 需要在hash匹配后, 进行一次字符的比对, 这就是Las Vegas版本的RK算法。而Monte Carlo版本的RK算法通过把映射hash表的Q值取尽可能大(比如long值$10^{20}$), 使得hash冲突概率降得尽可能低(如低至$1/Q = 10^{-20}$).
boolean check(int i) // Monte Carlo (See text.)
{ return true; } // For Las Vegas, check pat vs txt(i..i-M+1).
二者对比:
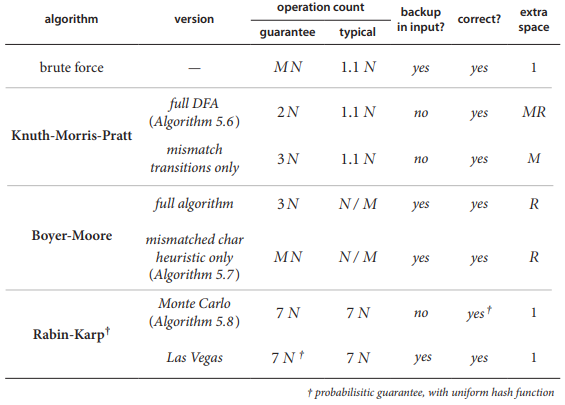
- Monte Carlo version. Return match if hash match. Always runs in linear time. Extremely likely to return correct answer (but not always!).
- Las Vegas version. Check for substring match if hash match; continue search if false collision.Always returns correct answer. Extremely likely to run in linear time (but worst case is M N).
In theory, if
Qis a sufficiently large random prime (about $M N^2$), then the probability of a false collision is about1 / N. In practice, chooseQto be a large prime (but not so large to cause overflow). Under reasonable assumptions, probability of a collision is about1 / Q.
最长回文子串
字符串哈希还可以用于计算判断最长回文子串,需要分别预处理正着和倒着的哈希值; 判断是否可行时枚举回文中心(对称轴),哈希判断两侧是否相等。
总结
 算法可以拓展到二维模式匹配, 多模式匹配等问题.
算法可以拓展到二维模式匹配, 多模式匹配等问题.