Survey: https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.00388v4
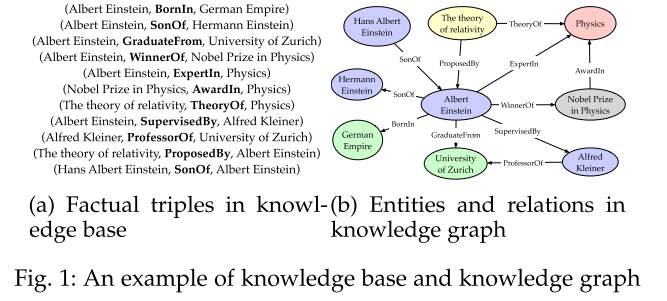
A knowledge graph is a structured representation of facts, consisting of entities, relationships and semantic descriptions.
- Entities can be real-world objects and abstract concepts,
- Relationships represent the relation between entities,
- Semantic descriptions of entities and their relationships contain types and properties with a well-defined meaning
G: A knowledge graph F: A set of facts (h, r, t): A triple of head, relation and tail $(\mathbf{h}, \mathbf{r}, \mathbf{t})$: Embedding of head, relation and tail
Definition 1 (Ehrlinger and W¨oß [7]). A knowledge graph acquires and integrates information into an ontology and applies a reasoner to derive new knowledge.
Definition 2 (Wang et al. [8]). A knowledge graph is a multi- relational graph composed of entities and relations which are regarded as nodes and different types of edges, respectively.
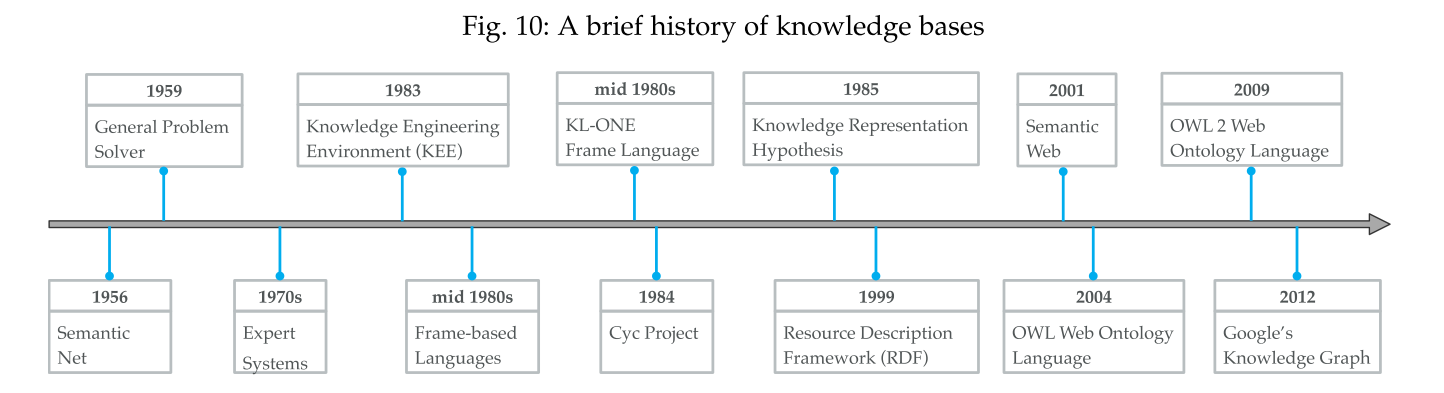
KB vs KG
The term of knowledge graph is synonymous with knowledge base with a minor difference. A knowledge graph can be viewed as a graph when considering its graph structure. When it involves formal semantics, it can be taken as a knowledge base for interpretation and inference over facts
Data Structure
- Resource Description Framework (RDF):(head, relation, tail) or (subject, predicate, object)
- Web Ontology Language (OWL)
- Directed Graph:with nodes as entities and edges as relations
KNOWLEDGE-AWARE APPLICATIONS
Question Answering
knowledge-graph-based question answering (KG-QA) an- swers natural language questions with facts from knowledge graphs. Neural
- Single-fact QA Taking knowledge graph as an external intellectual source, simple factoid QA or single-fact QA is to answer simple question involving with a single knowledge graph fact
- Multi-hop Reasoning
Recommender Systems
Integrating knowledge graphs as external information enables recommendation systems to have the ability of commonsense reasoning.
By injecting knowledge-graph-based side information such as entities, relations, and attributes, many efforts work on embedding-based regularization to improve recommendation.
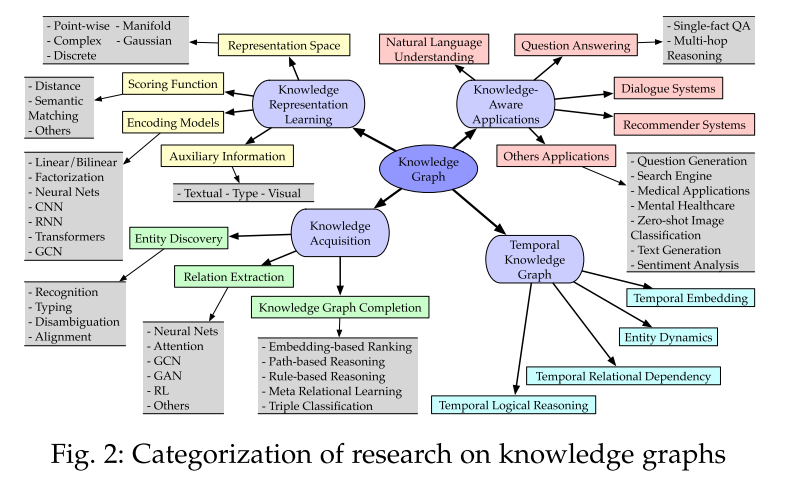
knowledge representation learning (KRL)
focus on knowledge representation learning (KRL) or knowledge graph embedding (KGE) by mapping entities and relations into low-dimensional vectors while capturing their semantic meanings
- representation space in which the relations and entities are represented;
- scoring function for measuring the plausibility of factual triples;
- encoding models for representing and learning relational interactions;
- auxiliary information to be incorporated into the embedding methods. Representation
3.1 Representation Space
3.1.1 Point-Wise Space Point-wise
TransE: represents entities and relations in d-dimension vector space
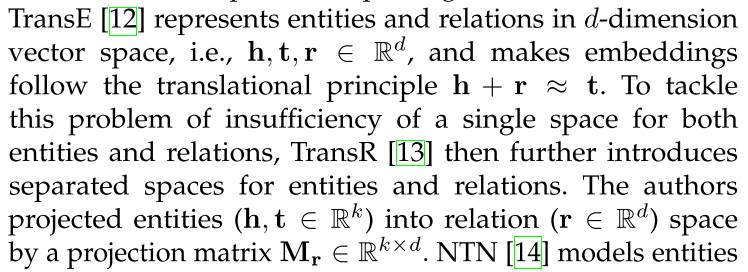
NTN: models entities across multiple dimensions by a bilinear tensor neural layer.
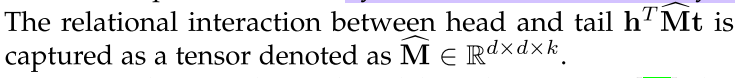
3.1.2 ComplexVector Space Instead
3.1.3 Gaussian Distribution
Inspired by Gaussian word embedding, the density-based embedding model KG2E [21] introduces Gaussian distribution to deal with the (un)certainties of entities and relations.
3.1.4 Manifold and Group
A manifold is a topological space which could be defined as a set of points with neighborhoods by the set theory, while the group is algebraic structures defined in abstract algebra.
3.2 Scoring Function
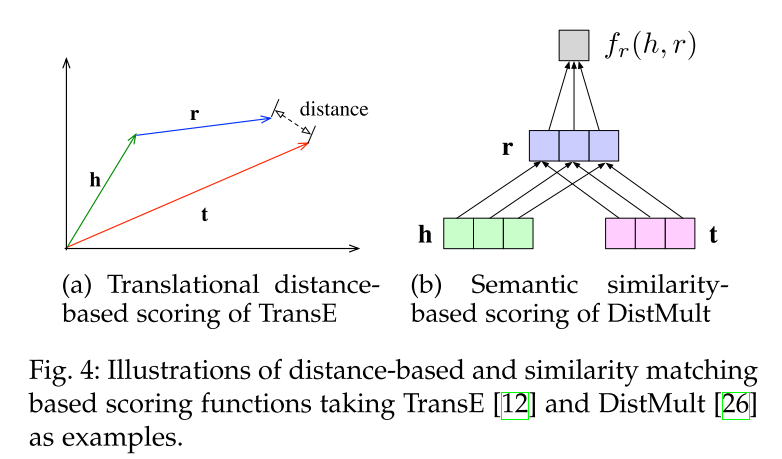
Distance-based scoring function measures the plausibility of facts by calculating the distance between entities, where addictive translation with relations as h + r ≈ t is widely used
Semantic similarity based scoring measures the plausibility of facts by semantic matching, which usually adopts multiplicative formulation $\mathbf{h}^{\top} \mathbf{M}_{r} \approx \mathbf{t}^{\top}$
3.2.1 Distance-based Scoring Function
calculate the Euclidean distance between the relational projection of entities.
Structural Embedding (SE) :

A more intensively used principle is the translation-based scoring function that aims to learn embeddings by representing relations as translations from head to tail entities.
TransE:

TransH:
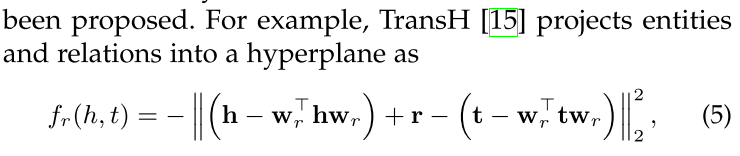
TransR:
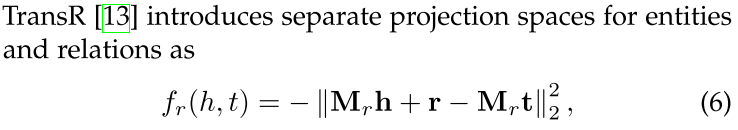
TransD:
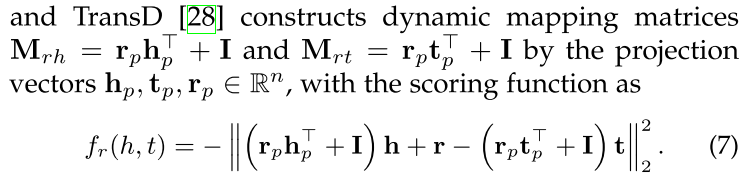
TransA:

TransF:

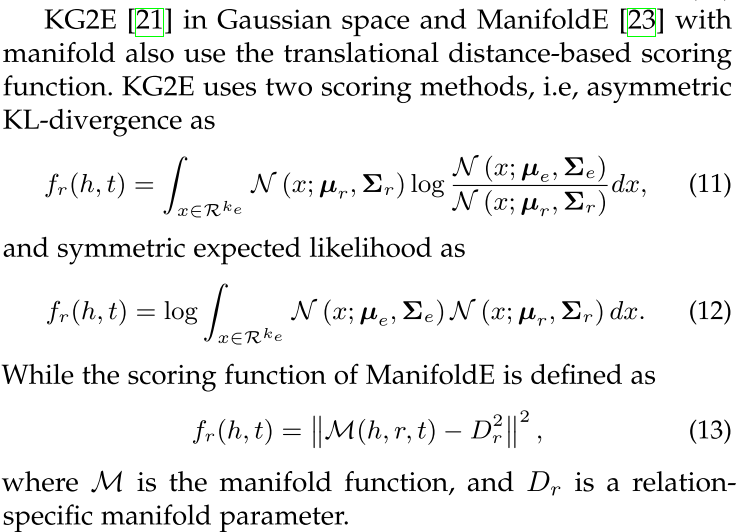
KG2E:
3.2.2 Semantic Matching
DistMult: By restricting relation matrixMr to be diagonal for multi-relational representation learning
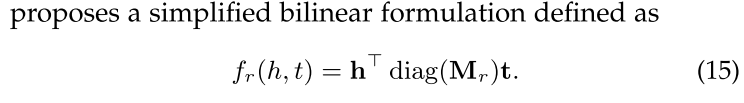
3.3 Encoding Models
3.3.1 Linear/Bilinear Models
- applying linear operation $g_{r}(\mathbf{h}, \mathbf{t})=\mathbf{M}_{r}^{T}\left(\begin{array}{c} \mathbf{h} \\ \mathbf{t} \end{array}\right)$
- bilinear transformation operations $f_{r}(h, t)=\mathbf{h}^{\top} \mathbf{M}_{r} \mathbf{t}$
Y. Wang, R. Gemulla, and H. Li, “On multi-relational link prediction with bilinear models,” showed that the ensembles of multiple linear models can improve the prediction performance through experiments
3.3.2 Factorization Models
Factorization methods formulated KRL models as three-way tensor $X$ decomposition. A general principle of tensor factorization can be denoted as $X_{h r t} \approx \mathbf{h}^{\top} \mathbf{M}_{r} \mathbf{t}$
3.3.3 Neural Networks
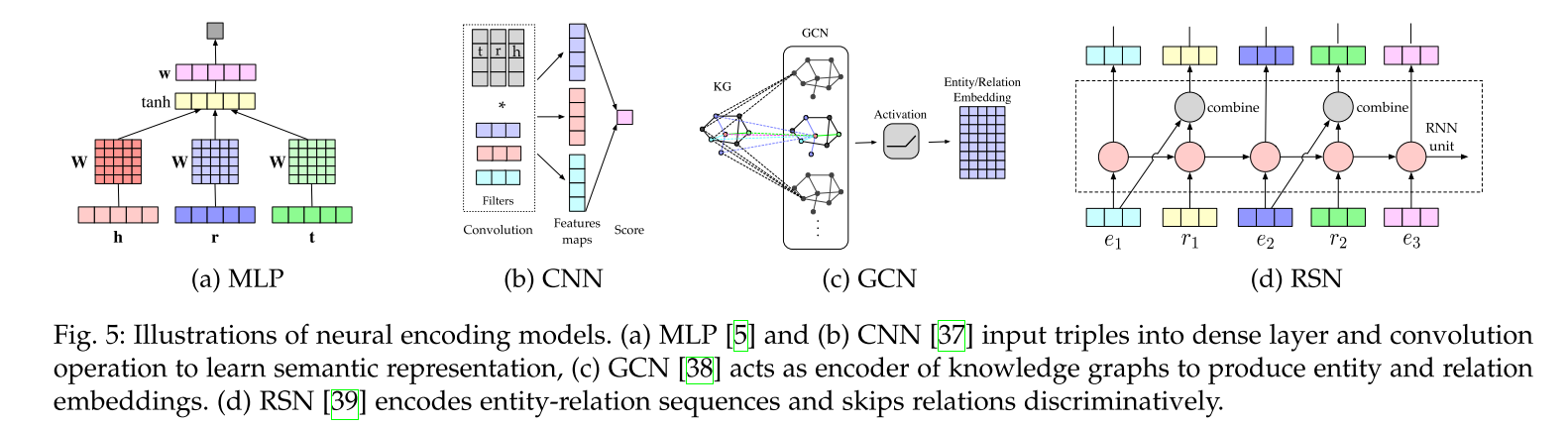
Encoding models with linear/bilinear blocks can also be modeled using neural networks.
Generally, they take entities and/or relations into deep neural networks and compute a semantic matching score.

Convolutional Neural Networks

RSN: a recurrent skip mechanism to enhance
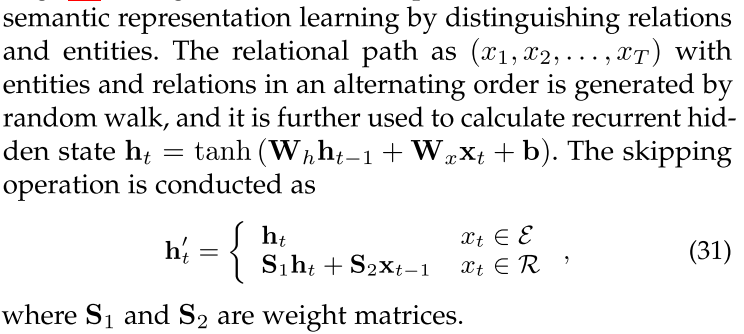
Transformers: KG-BERT
Graph Neural Networks: GNNs for learning connectivity structure under an encoder-decoder framework.
3.4 Embedding with Auxiliary Information
3.4.1 Textual Description
The challenge of KRL with textual description is to embed both structured knowledge and unstructured textual information in the same space. Wang
3.4.2 Type Information
Entities are represented with hierarchical classes or types, and consequently, relations with semantic types
3.4.3 Visual Information
knowledge acquisition tasks
- knowledge graph completion (KGC): expanding existing knowledge graphs
- embedding-based ranking,
- relation path reasoning,
- rule-based reasoning
- meta relational learning
- entity discovery
- recognition,
- disambiguation,
- typing
- alignment
- Relation extraction
- triple classification,
4.1 Knowledge Graph Completion
Knowledge graph completion completes missing links between existing entities or infers entities given entity and relation queries, to add new triples to a knowledge graph. Typical subtasks include link prediction, entity prediction and relation prediction.
- embedding-based methods: failed to capture multi-step relationships
- relation path inference: explore multi-step relation paths
- rule-based reasoning: incorporate logical rules
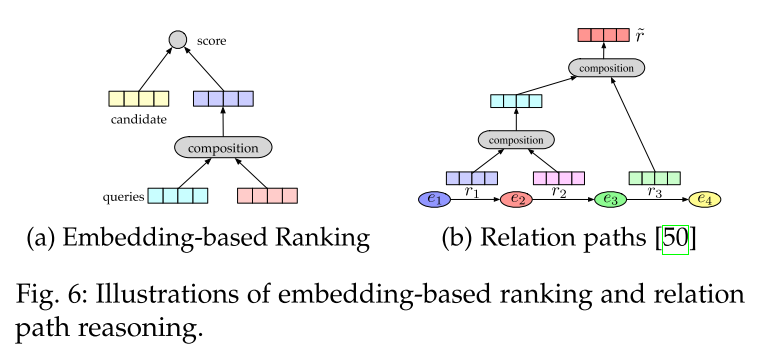
4.1.1 Embedding-based Models
- learn embedding vectors based on existing triples,
- then replace tail entity or head entity with each entity e ∈ E to calculate scores of all the candidate entities and rank the top k entities.
4.1.2 Relation Path Reasoning
Random walk inference has been widely investigated, for example, the Path-Ranking Algorithm (PRA) [69] chooses relational path under a combination of path constraints, and conducts maximum-likelihood classification
4.1.3 RL-basedPath Finding
Deep reinforcement learning (RL) is introduced for multi- hop reasoning by formulating path-finding between entity pairs as sequential decision making, specifically a Markov decision process (MDP). The policy-based RL agent learns to find a step of relation to extend the reasoning paths via the interaction between the knowledge graph environment, where the policy gradient is utilized for training RL agents.
4.1.4 Rule-based Reasoning
logical rule learning
4.1.5 Meta Relational Learning
The long-tail phenomena exist in the relations of knowledge graphs. Meanwhile, the real-world scenario of knowledge is dynamic, where unseen triples are usually acquired.
meta relational learning or few-shot relational learning, requires models to predict new relational facts with only a very few samples.
4.1.6 Triple Classification
Triple classification is to determine whether facts are correct in testing data, which is typically regarded as a binary classification problem.
4.2 Entity Discovery
4.2.1 Entity Recognition
4.2.2 Entity Typing
Entity typing includes coarse and fine-grained types, while the latter one uses a tree-structured type category and is typically regarded as multi-class and multi-label classifi- cation.
4.2.3 Entity Disambiguation
or entity linking is a unified task which links entity mentions to the corresponding entities in a knowledge graph.
4.2.4 Entity Alignment
aims to fuse knowledge among heterogeneous knowledge graphs. In practice, a small set of alignment seeds (i.e., synonymous entities appear in different knowledge graphs) is given to start the alignment process.
Embedding-based alignment calculates the similarity between embeddings of a pair of entities.
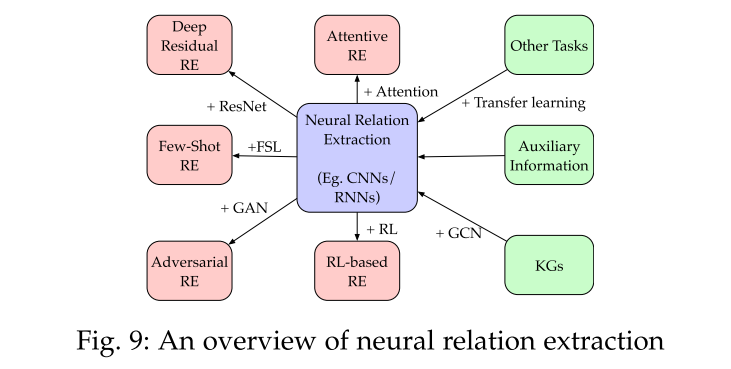
4.3 Relation Extraction
distant supervision, also referred as weak supervision or self supervision, uses heuristic matching to create training data by assuming that sentences containing the same entity mentions may express the same relation under the supervision of a relational database.
Temporal Knowledge Graphs
incorporate temporal information for representation learning.
- temporal embedding,
- entity dynamics,
- temporal relational dependency,
- temporal logical reasoning.
Knowledge-aware Applications
include natural language understanding (NLU), question answering, recommendation systems, and miscellaneous real-world tasks, which inject knowledge to improve representation learning.
Open Knowledge Bases or Ontologies
WordNet, DBpedia, YAGO, and Freebase