A Lite BERT
BERT(Devlin et al., 2019)的参数很多, 模型很大, 内存消耗很大, 在分布式计算中的通信开销很大.
但是BERT的高内存消耗边际收益并不高, 如果继续增大BERT-large这种大模型的隐含层大小, 模型效果不升反降.
针对这些问题, 启发于mobilenet, Alert使用了两种减少参数的方法来降低模型大小和提高训练速度, 分别是Factorized embedding parameterization和Cross-layer parameter sharing. 这些设计让ALBERT增加参数大小的边界收益远远大于BERT.
除此之外, 在句子关系任务上抛弃了bert的nsp任务, 改为sop任务.
整体而言, ALBERT是当前众多BERT系列模型的集大成者, 其思路值得学习, 代码也写得很清楚. 下面仔细过一遍.
Factorized embedding parameterization
BERT以及后续的XLNet(Yang et al., 2019), RoBERTa(Liu et al., 2019)等, WordPiece embedding的维度E是和隐层维度H绑定的. WordPiece embedding本意是学习context-independent的表达,而hidden-layer旨在学习context-dependent的表达。将WordPiece embedding大小E与隐层大小H解绑,可以更有效地利用建模所需的总模型参数.
从实用性的角度看, 这样可以减少词汇量对模型大小的影响. 在NLP中词汇量一般都很大, 所以这个解绑收益是很明显的.
具体的做法就是对embedding进行因式分解, 把非常大的单词embedding分解成两个小的矩阵, O(V × H)变成O(V × E + E × H), 可以显著减少单词映射embedding的参数量. 这个在topic models一文中的隐变量模型中类似的思路体现.
Cross-layer parameter sharing
各个 transformer blocks 所有参数共享, 这样参数不再随着模型层数加深而增大.
No Dropout
RoBERTA指出BERT一系列模型都是"欠拟合"的, 所以干脆直接关掉dropout, 那么在ALBERT中也是去掉 Dropout 层可以显著减少临时变量对内存的占用. 同时论文发现, Dropout会损害大型Transformer-based模型的性能。
Sentence-order Prediction (SOP)
BERT使用的NSP任务是一种二分类loss,预测原始文本中是否有两个片段连续出现,通过从训练语料库中获取连续片段来创建正样本;通过将不同文档的片段配对作为负样本.
在RoBERTA等改进型的论文中都指出, NSP的表现不是很稳定, 所以RoBERTa直接就去掉了NSP任务.
而ALBERT推测, NSP任务对下游任务提升不稳定的原因在于NSP任务学习难度不够高(相对于MLM任务)。NSP本质是融合了topic prediction主题预测和coherence prediction两个任务。Coherence prediction是核心的任务, 可以学习inter-sentence信息. 主题预测, 也就是学习两个句子是否来自同一段原文, 则相对容易得多,并且与使用MLM损失学习的内容重叠更多。
所以我们需要一个更专注于coherence prediction的sentence level任务, 比如ALBERT中用到的SOP.
SOP的正样本采样方法和BERT一样, 但负样本改为倒置顺序的两句话, 这迫使模型学习关于discourse-level coherence properties的细粒度区别。
Transformer实现
Bert和Albert的核心模型架构都是Transformer encoder, 包括用于编码context的Multi-headed self attention层, 用于计算非线性层间特征的Feed-forward layers, 和用于加深网络深度, 降低训练难度的Layer norm and residuals. 除此之外, 还有Positional embeddings用来编码相对位置信息.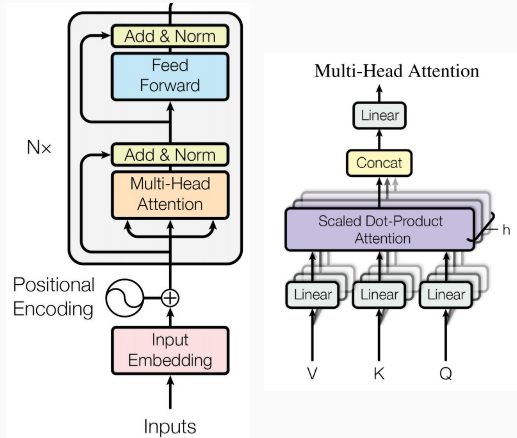
Transformer由一个个结构相同的blocks堆叠而成, 每一个block可以简单理解为一个注意力层+全连接层+残差网络, API是这样:
def attention_ffn_block(layer_input,
hidden_size=768,
attention_mask=None,
num_attention_heads=1,
attention_head_size=64,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0,
intermediate_size=3072,
intermediate_act_fn=None,
initializer_range=0.02,
hidden_dropout_prob=0.0):
"""A network with attention-ffn as sub-block.
Args:
layer_input: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, from_seq_length,
from_width].
hidden_size: (optional) int, size of hidden layer.
attention_mask: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size,
from_seq_length, to_seq_length]. The values should be 1 or 0. The
attention scores will effectively be set to -infinity for any positions in
the mask that are 0, and will be unchanged for positions that are 1.
num_attention_heads: int. Number of attention heads.
attention_head_size: int. Size of attention head.
attention_probs_dropout_prob: float. dropout probability for attention_layer
intermediate_size: int. Size of intermediate hidden layer.
intermediate_act_fn: (optional) Activation function for the intermediate
layer.
initializer_range: float. Range of the weight initializer.
hidden_dropout_prob: (optional) float. Dropout probability of the hidden
layer.
Returns:
layer output
"""
其中最开始是注意力层, 并在输出后面接残差, 最后正则化:
with tf.variable_scope("attention_1"):
with tf.variable_scope("self"):
attention_output = attention_layer(
from_tensor=layer_input,
to_tensor=layer_input,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=attention_probs_dropout_prob,
initializer_range=initializer_range)
# Run a linear projection of `hidden_size` then add a residual
# with `layer_input`.
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
attention_output = dense_layer_3d_proj(
attention_output,
hidden_size,
attention_head_size,
create_initializer(initializer_range),
None,
name="dense")
attention_output = dropout(attention_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
attention_output = layer_norm(attention_output + layer_input)
其中用到的点乘注意力和多头注意力直接使用上一篇Transformer & Self-Attention (多头)自注意力编码中的方法.
然后就是feed forward layer, 在输出层之前加入了一个升维的中间层intermediate, 并应用激活函数(在这里是gelu), 末尾的输出网络没有激活函数, 只负责把输出映射回transformer的隐含层维度大小, 最后同样加上残差和正则化. 这种扩张-变换-压缩的范式, 是借鉴了mobilenet中的思路, 在需要使用ReLU的卷积层中,将channel数扩张到足够大,再进行激活,被认为可以降低激活层的信息损失。:
with tf.variable_scope("ffn_1"):
with tf.variable_scope("intermediate"):
intermediate_output = dense_layer_2d(
attention_output,
intermediate_size,
create_initializer(initializer_range),
intermediate_act_fn,
num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads,
name="dense")
with tf.variable_scope("output"):
ffn_output = dense_layer_2d(
intermediate_output,
hidden_size,
create_initializer(initializer_range),
None,
num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads,
name="dense")
ffn_output = dropout(ffn_output, hidden_dropout_prob)
ffn_output = layer_norm(ffn_output + attention_output)
return ffn_output
其中用到的dense_layer_2d就是一个基本的神经网络$y=f(Wx+b)$, 其中$f()$是激活函数:
def dense_layer_2d(input_tensor,
output_size,
initializer,
activation,
num_attention_heads=1,
name=None):
"""A dense layer with 2D kernel.
Args:
input_tensor: Float tensor with rank 3.
output_size: The size of output dimension.
initializer: Kernel initializer.
activation: Activation function.
num_attention_heads: number of attention head in attention layer.
name: The name scope of this layer.
Returns:
float logits Tensor.
"""
del num_attention_heads # unused
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor)
hidden_size = input_shape[2]
with tf.variable_scope(name):
w = tf.get_variable(
name="kernel",
shape=[hidden_size, output_size],
initializer=initializer)
b = tf.get_variable(
name="bias", shape=[output_size], initializer=tf.zeros_initializer)
ret = tf.einsum("BFH,HO->BFO", input_tensor, w)
ret += b
if activation is not None:
return activation(ret)
else:
return ret
一个完整的transformer模块, 核心是由多个attention_ffn_block堆叠而成, 同时注意设定reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE来实现Cross-layer parameter sharing, 设定num_hidden_groups=1就可以让所有层都共享参数.
def transformer_model(input_tensor,
attention_mask=None,
hidden_size=768,
num_hidden_layers=12,
num_hidden_groups=12,
num_attention_heads=12,
intermediate_size=3072,
inner_group_num=1,
intermediate_act_fn="gelu",
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
initializer_range=0.02,
do_return_all_layers=False):
"""Multi-headed, multi-layer Transformer from "Attention is All You Need".
This is almost an exact implementation of the original Transformer encoder.
See the original paper:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
Also see:
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensor2tensor/blob/master/tensor2tensor/models/transformer.py
Args:
input_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size].
attention_mask: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length,
seq_length], with 1 for positions that can be attended to and 0 in
positions that should not be.
hidden_size: int. Hidden size of the Transformer.
num_hidden_layers: int. Number of layers (blocks) in the Transformer.
num_hidden_groups: int. Number of group for the hidden layers, parameters
in the same group are shared.
num_attention_heads: int. Number of attention heads in the Transformer.
intermediate_size: int. The size of the "intermediate" (a.k.a., feed
forward) layer.
inner_group_num: int, number of inner repetition of attention and ffn.
intermediate_act_fn: function. The non-linear activation function to apply
to the output of the intermediate/feed-forward layer.
hidden_dropout_prob: float. Dropout probability for the hidden layers.
attention_probs_dropout_prob: float. Dropout probability of the attention
probabilities.
initializer_range: float. Range of the initializer (stddev of truncated
normal).
do_return_all_layers: Whether to also return all layers or just the final
layer.
Returns:
float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size], the final
hidden layer of the Transformer.
Raises:
ValueError: A Tensor shape or parameter is invalid.
"""
if hidden_size % num_attention_heads != 0:
raise ValueError(
"The hidden size (%d) is not a multiple of the number of attention "
"heads (%d)" % (hidden_size, num_attention_heads))
attention_head_size = hidden_size // num_attention_heads
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3)
input_width = input_shape[2]
all_layer_outputs = []
if input_width != hidden_size:
prev_output = dense_layer_2d(
input_tensor, hidden_size, create_initializer(initializer_range),
None, name="embedding_hidden_mapping_in")
else:
prev_output = input_tensor
with tf.variable_scope("transformer", reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
for layer_idx in range(num_hidden_layers):
group_idx = int(layer_idx / num_hidden_layers * num_hidden_groups)
with tf.variable_scope("group_%d" % group_idx):
with tf.name_scope("layer_%d" % layer_idx):
layer_output = prev_output
for inner_group_idx in range(inner_group_num):
with tf.variable_scope("inner_group_%d" % inner_group_idx):
layer_output = attention_ffn_block(
layer_output, hidden_size, attention_mask,
num_attention_heads, attention_head_size,
attention_probs_dropout_prob, intermediate_size,
intermediate_act_fn, initializer_range, hidden_dropout_prob)
prev_output = layer_output
all_layer_outputs.append(layer_output)
if do_return_all_layers:
return all_layer_outputs
else:
return all_layer_outputs[-1]
Factorized Embedding实现
首先是需要embedding的因式分解, embedding_lookup输出的是V x E matrix, 其中E就是embedding_size:
def embedding_lookup(input_ids,
vocab_size,
embedding_size=128,
initializer_range=0.02,
word_embedding_name="word_embeddings",
use_one_hot_embeddings=False):
"""Looks up words embeddings for id tensor.
Args:
input_ids: int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length] containing word
ids.
vocab_size: int. Size of the embedding vocabulary.
embedding_size: int. Width of the word embeddings.
initializer_range: float. Embedding initialization range.
word_embedding_name: string. Name of the embedding table.
use_one_hot_embeddings: bool. If True, use one-hot method for word
embeddings. If False, use `tf.nn.embedding_lookup()`.
Returns:
float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size].
"""
# This function assumes that the input is of shape [batch_size, seq_length,
# num_inputs].
#
# If the input is a 2D tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length], we
# reshape to [batch_size, seq_length, 1].
if input_ids.shape.ndims == 2:
input_ids = tf.expand_dims(input_ids, axis=[-1])
embedding_table = tf.get_variable(
name=word_embedding_name,
shape=[vocab_size, embedding_size],
initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
if use_one_hot_embeddings:
flat_input_ids = tf.reshape(input_ids, [-1])
one_hot_input_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_input_ids, depth=vocab_size)
output = tf.matmul(one_hot_input_ids, embedding_table)
else:
output = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_table, input_ids)
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids)
output = tf.reshape(output,
input_shape[0:-1] + [input_shape[-1] * embedding_size])
return (output, embedding_table)
把embedding映射回隐层大小E x H, 依靠的是上面定义的transformer_model中的
if input_width != hidden_size:
prev_output = dense_layer_2d(
input_tensor, hidden_size, create_initializer(initializer_range),
None, name="embedding_hidden_mapping_in")
ALBERT模型搭建
大体框架就是embeddings+encoder+pooler output, 其中encoder就是transformerblocks的堆叠:
class AlbertModel(object):
"""BERT model ("Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers").
"""
def __init__(self,
config,
is_training,
input_ids,
input_mask=None,
token_type_ids=None,
use_one_hot_embeddings=False,
scope=None):
"""Constructor for AlbertModel.
Args:
config: `AlbertConfig` instance.
is_training: bool. true for training model, false for eval model. Controls
whether dropout will be applied.
input_ids: int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length].
input_mask: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length].
token_type_ids: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length].
use_one_hot_embeddings: (optional) bool. Whether to use one-hot word
embeddings or tf.embedding_lookup() for the word embeddings.
scope: (optional) variable scope. Defaults to "bert".
Raises:
ValueError: The config is invalid or one of the input tensor shapes
is invalid.
"""
config = copy.deepcopy(config)
if not is_training:
config.hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0
config.attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids, expected_rank=2)
batch_size = input_shape[0]
seq_length = input_shape[1]
if input_mask is None:
input_mask = tf.ones(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32)
if token_type_ids is None:
token_type_ids = tf.zeros(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32)
with tf.variable_scope(scope, default_name="bert"):
with tf.variable_scope("embeddings"):
# Perform embedding lookup on the word ids.
(self.word_embedding_output,
self.output_embedding_table) = embedding_lookup(
input_ids=input_ids,
vocab_size=config.vocab_size,
embedding_size=config.embedding_size,
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
word_embedding_name="word_embeddings",
use_one_hot_embeddings=use_one_hot_embeddings)
# Add positional embeddings and token type embeddings, then layer
# normalize and perform dropout.
self.embedding_output = embedding_postprocessor(
input_tensor=self.word_embedding_output,
use_token_type=True,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
token_type_vocab_size=config.type_vocab_size,
token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings",
use_position_embeddings=True,
position_embedding_name="position_embeddings",
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
max_position_embeddings=config.max_position_embeddings,
dropout_prob=config.hidden_dropout_prob)
with tf.variable_scope("encoder"):
# Run the stacked transformer.
# `sequence_output` shape = [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size].
self.all_encoder_layers = transformer_model(
input_tensor=self.embedding_output,
attention_mask=input_mask,
hidden_size=config.hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=config.num_hidden_layers,
num_hidden_groups=config.num_hidden_groups,
num_attention_heads=config.num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=config.intermediate_size,
inner_group_num=config.inner_group_num,
intermediate_act_fn=get_activation(config.hidden_act),
hidden_dropout_prob=config.hidden_dropout_prob,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=config.attention_probs_dropout_prob,
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
do_return_all_layers=True)
self.sequence_output = self.all_encoder_layers[-1]
# The "pooler" converts the encoded sequence tensor of shape
# [batch_size, seq_length, hidden_size] to a tensor of shape
# [batch_size, hidden_size]. This is necessary for segment-level
# (or segment-pair-level) classification tasks where we need a fixed
# dimensional representation of the segment.
with tf.variable_scope("pooler"):
# We "pool" the model by simply taking the hidden state corresponding
# to the first token. We assume that this has been pre-trained
first_token_tensor = tf.squeeze(self.sequence_output[:, 0:1, :], axis=1)
self.pooled_output = tf.layers.dense(
first_token_tensor,
config.hidden_size,
activation=tf.tanh,
kernel_initializer=create_initializer(config.initializer_range))
再附上官网的API介绍:
# Already been converted from strings into ids
input_ids = tf.constant([[31, 51, 99], [15, 5, 0]])
input_mask = tf.constant([[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0]])
token_type_ids = tf.constant([[0, 0, 1], [0, 2, 0]])
config = modeling.AlbertConfig(vocab_size=32000, hidden_size=512,
num_hidden_layers=8, num_attention_heads=6, intermediate_size=1024)
model = modeling.AlbertModel(config=config, is_training=True,
input_ids=input_ids, input_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)
label_embeddings = tf.get_variable(...)
pooled_output = model.get_pooled_output()
logits = tf.matmul(pooled_output, label_embeddings)
...