2019, ACL
data: TWITTER, WEIBO
links: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/N19-1163, https://github.com/DeepBrainAI/ERD
task: Rumour Detection
这篇文章采用GRU编码社交媒体posts stream,作为环境的状态表示;训练一个分类器以GRU的状态输出为输入,对文本做二分类判断是否是rumor。用DQN训练agent,根据状态做出是否启动rumor分类器进行判断,并根据分类结果对错给予奖惩。目标就是尽可能准尽可能早地预测出社交媒体posts是否是rumor。
Focuses on the task of rumour detection; particularly, we are in- terested in understanding how early we can detect them.
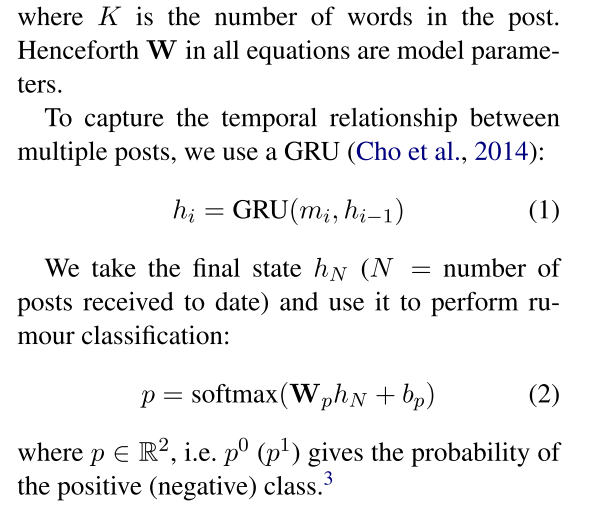
Our model treats social media posts (e.g. tweets) as a data stream and integrates reinforcement learning to learn the number minimum num- ber of posts required before we classify an event as a rumour.
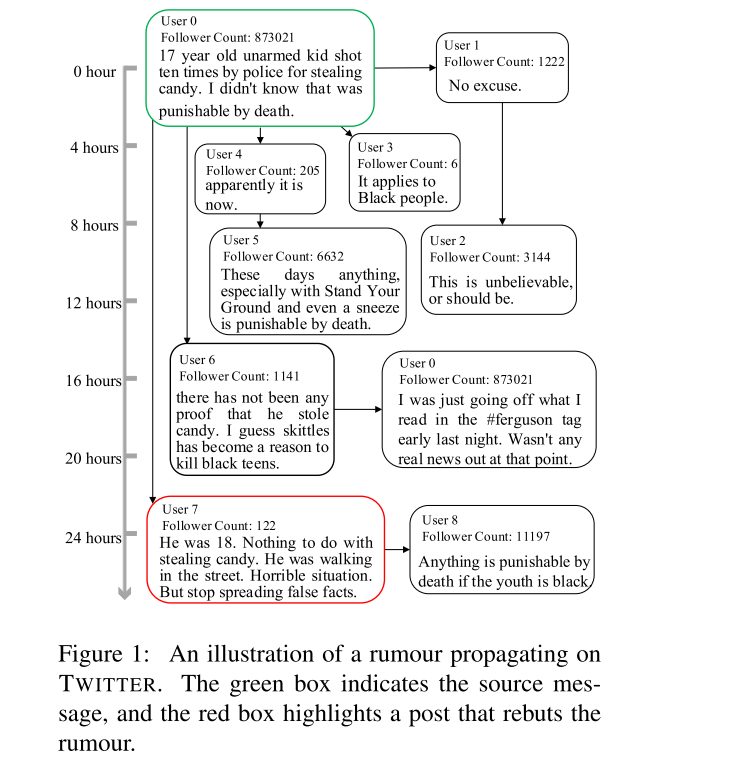
Let $E$ denote an event, and it consists of a series of relevant posts $x_i$, where $x_0$ denotes the source message and $x_T$ the last relevant message. The objective of early rumor detection is to make a classification decision whether E is a rumour as early as possible while keeping an acceptable detection accuracy.
3 Model Architecture
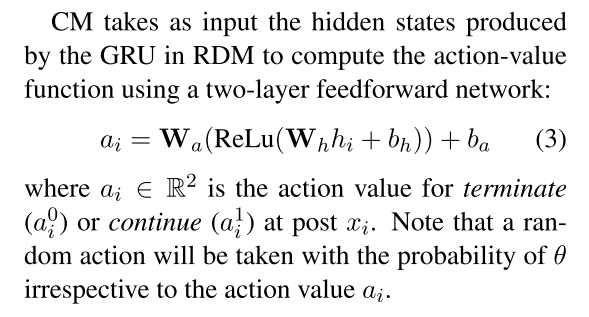
ERD has two modules: a rumour detection module (RDM) that classifies whether an event is a rumour, and a checkpoint module (CM) that decides when the rumour detec- tion module should be triggered.
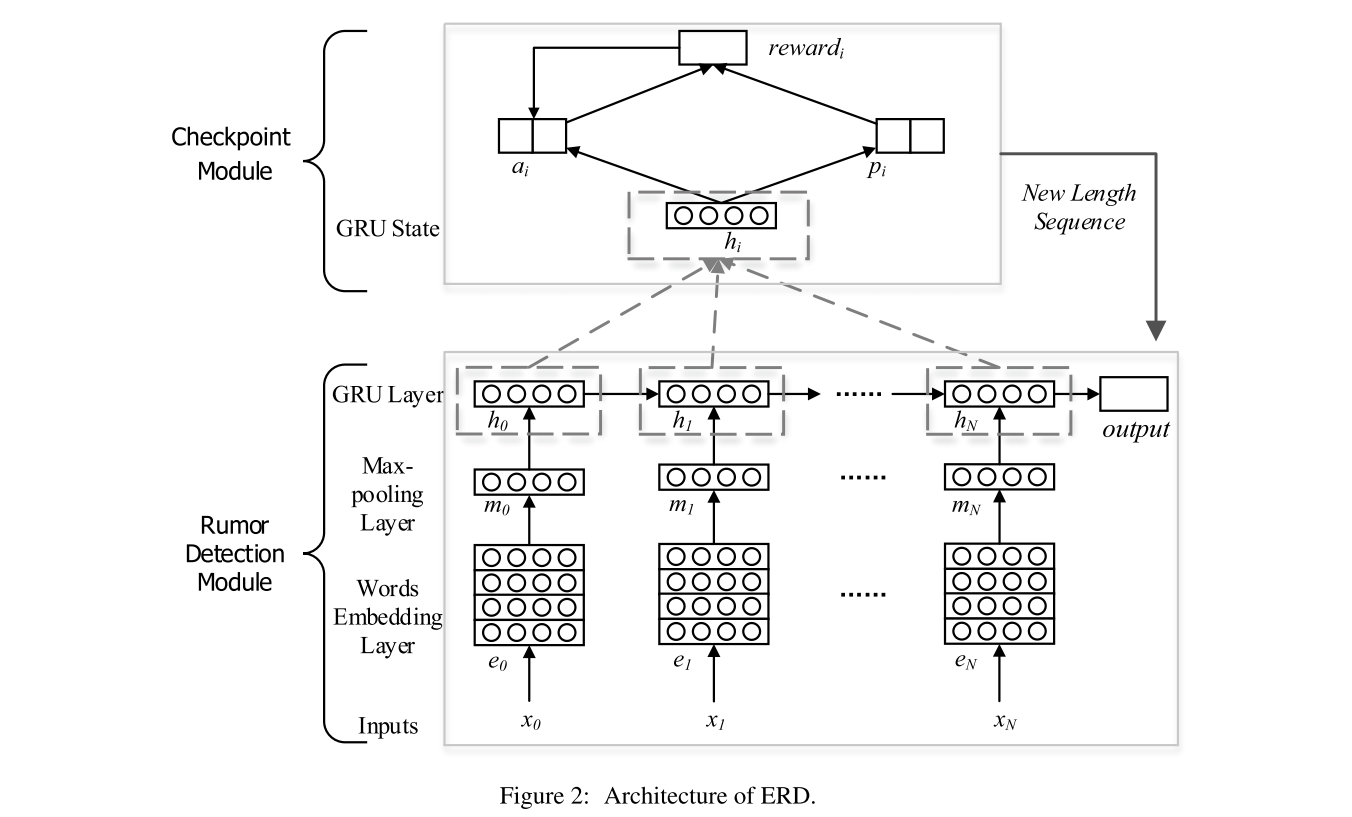
3.1 Rumor Detection Module (RDM)
RDM contains three layers: a word embedding layer that maps input words into vectors, a max- pooling layer that extracts important features of a post, and a GRU (Cho et al., 2014) that processes the sequential posts of an event.
word embedding layer: apply a max pooling operation
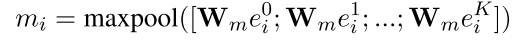
3.2 Checkpoint Module (CM)
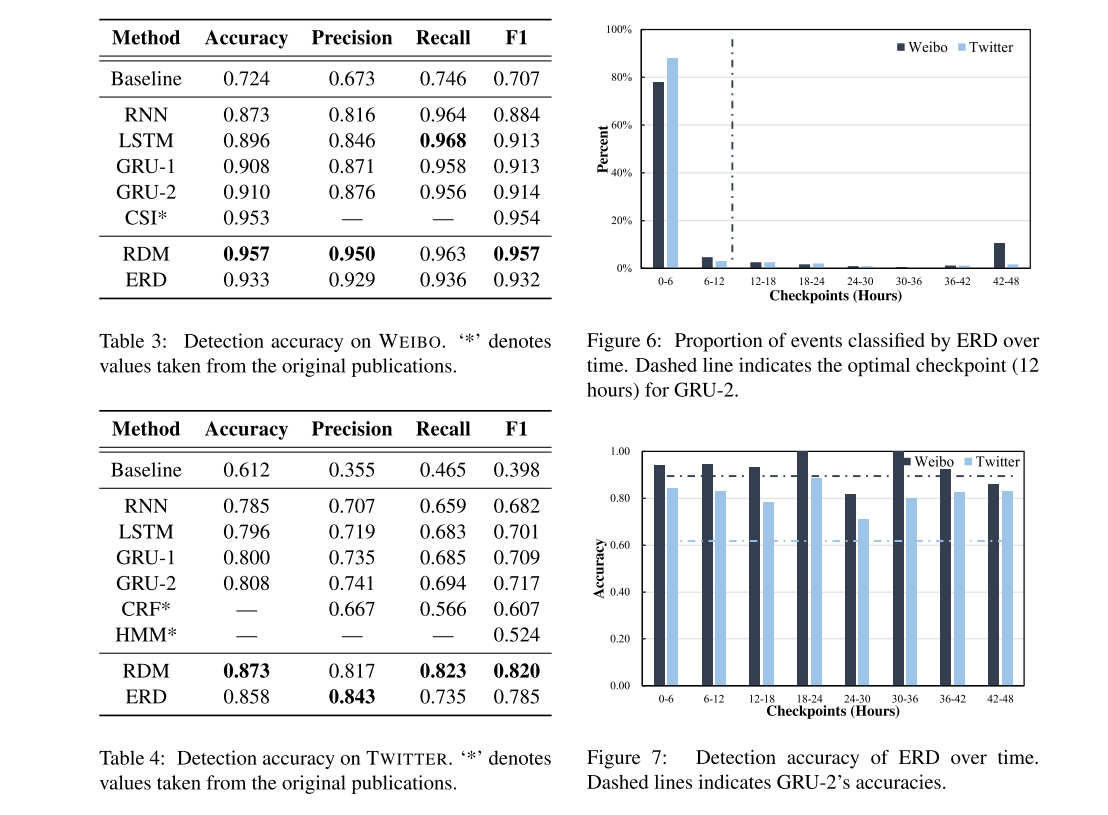
leverage deep Q-learning model to identify the optimal checkpoint

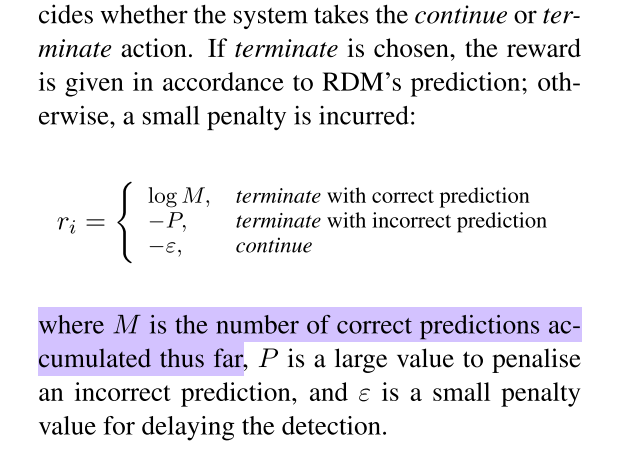
reward CM based on RDM’s accuracy and also penalise CM slightly every time it decides to not trigger RDM (and continue to monitor the event).
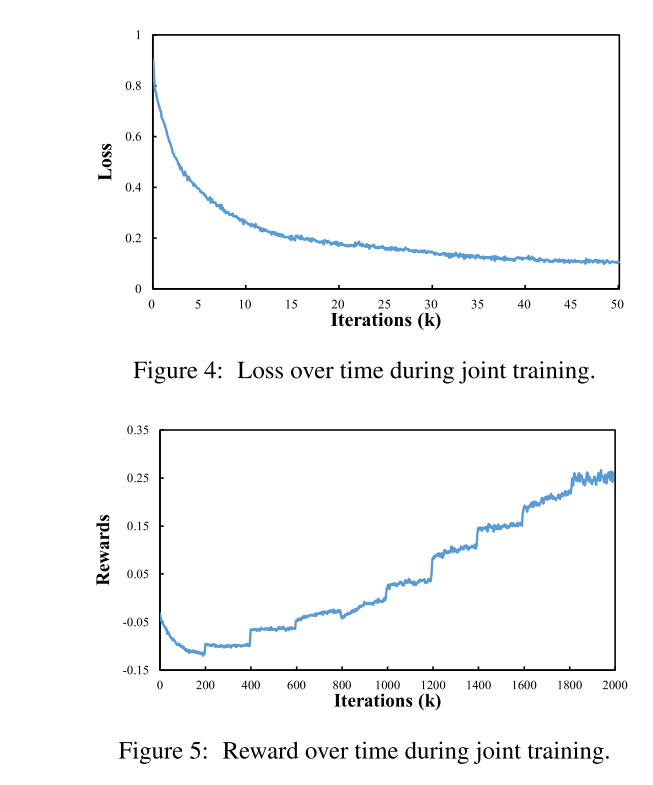
3.3 Joint Training
train both RDM and CM jointly, and the training process is similar to that of generative adversarial networks (Goodfellow et al., 2014). The checkpoint module serves as the generator for action sequences, while the detection module is the discriminator. A key contrast, however, is that the two modules are working cooperatively rather than adversarially.
- first pre-train RDM based on cross entropy
- then train train CM and RDM in an alternating fashion
- In each step of the training, new posts that have arrived and previous GRU states are first fed to the RDM to produce the new states. which will in turn be used by CM to calculate the action values.
- train RDM and CM in an alternating fashion for 1 epoch and 200K iterations respectively. We train CM for several iterations while keeping RDM’s parameters fixed, and then we move to train RDM for several iterations while keeping CM’s parameters fixed.
- Training converges when CM’s reward value stabilises between consecutive epochs.
DQN部分跟传统地DQN方法一样。
3.4 Bucketing Strategy
提高批处理效率. For processing efficiency purposes, instead of processing each incoming post individually, we experiment with several bucketing strategies that group posts together and process them in batches.
结果