The Line Patterns Recognition
A basic but important application of pattern recognition is to recognize line patterns in a given set of points. http://coursera.cs.princeton.edu/algs4/assignments/collinear.html. This blog will give a breif introduction to this problem and provide an enfficient solution. Codes available in algs4/collinear/src/
The problem could be described as: Given a set of n distinct points in the plane, find every (maximal) line segment that connects a subset of 4 or more of the points.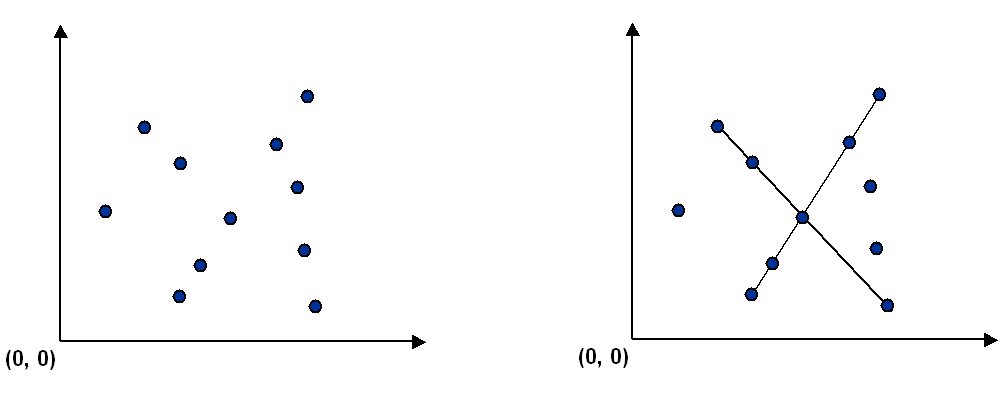 .
.
Point data type. an immutable data type Point that represents a point in the plane by implementing the following API:
public class Point implements Comparable<Point> {
public Point(int x, int y) // constructs the point (x, y)
public void draw() // draws this point
public void drawTo(Point that) // draws the line segment from this point to that point
public String toString() // string representation
public int compareTo(Point that) // compare two points by y-coordinates, breaking ties by x-coordinates
public double slopeTo(Point that) // the slope between this point and that point
public Comparator<Point> slopeOrder() // compare two points by slopes they make with this point
}
Line segment data type. To represent line segments in the plane, use the data type LineSegment.java, which has the following API:
public class LineSegment {
public LineSegment(Point p, Point q) // constructs the line segment between points p and q
public void draw() // draws this line segment
public String toString() // string representation
}
Apparently if using brute force, the order of growth of the running time of the program will be $n^4$ in the worst case.
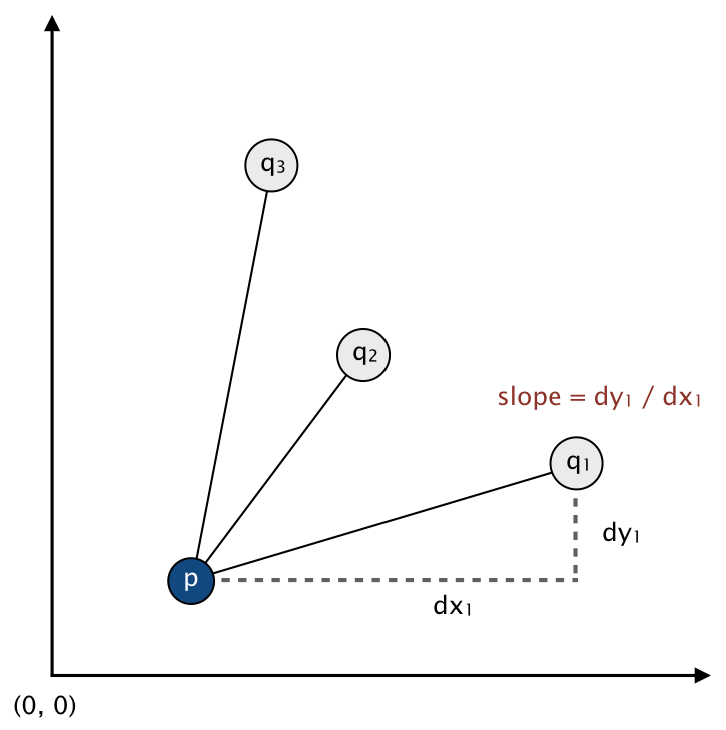
A faster, sorting-based solution: Given a point p, the following method determines whether p participates in a set of 4 or more collinear points.
- Think of p as the origin.
- For each other point q, determine the slope it makes with p.
- Sort the points according to the slopes they makes with p.
- Check if any 3 (or more) adjacent points in the sorted order have equal slopes with respect to p. If so, these points, together with p, are collinear.
Solution
There are two key points to get the order of growth of the running time to be $n^2\log n$ in the worst case, with space proportional to n plus the number of line segments returned, and work properly even if the input has 5 or more collinear points.
- Stable sort:
Arrays.sort()is guaranteed to be stable, so equal elements will not be reordered as a result of the sort. So the input points array is already sorted by points natural order once we sort the element at the first valid check step. - To avoid duplicate line segments, we need to check if new found collinear points pairs already exist in the LineSegment. If we loop over the LineSegment everytime we have a new line segments to check, this will results in large run time that will not satisfy the requirement. Instead, we need to make use of the inner features of the line patterns:
- Since the every possible segment is created by points it contains,
- and we iterate through the sorted Points array to find segment
- so every non-duplicate new segment is guaranteed to be created from its smallest point member
- any duplicate segment is created later by its other member other than the smallest