2020, ACL
data: ACE 05
task: Event Detection
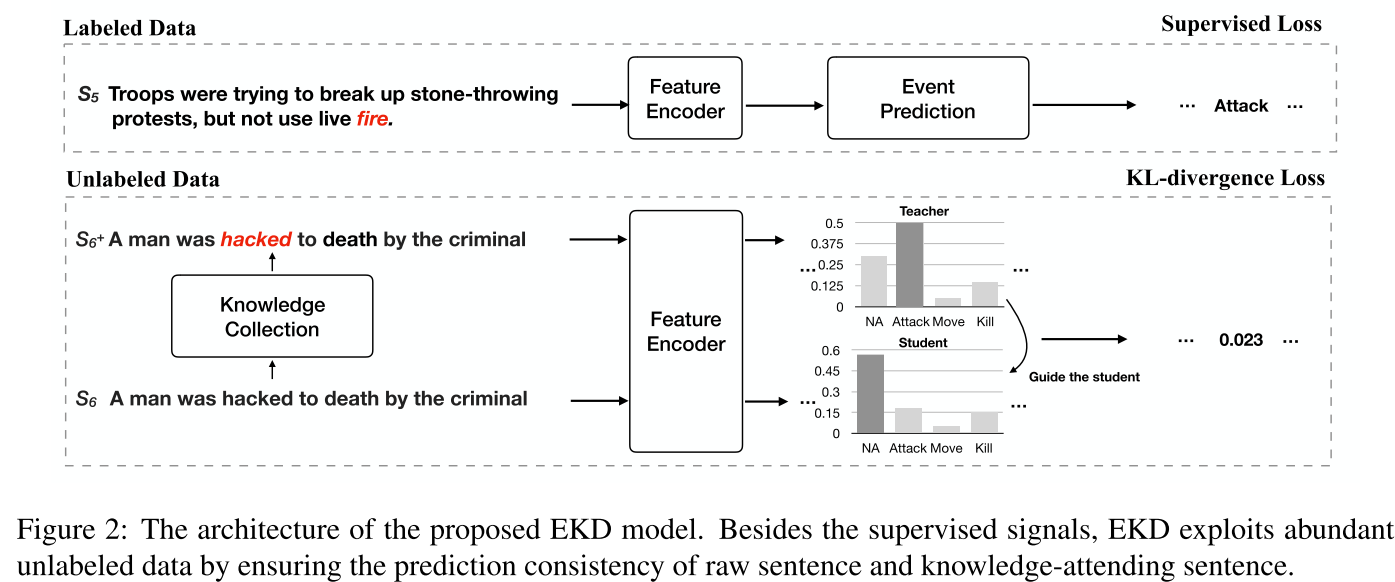
Propose a novel Enrichment Knowledge Distillation (EKD) model to efficiently distill external open-domain trigger knowledge to reduce the in-built biases to frequent trigger words in annotations.
- leverage the wealth of the open-domain trigger knowledge to improve ED
- propose a novel teacher-student model (EKD) that can learn from both labeled and unlabeled data

缺点
只能对付普遍情况, 即一般性的触发词; 但触发词不是在任何语境下都是触发词.
方法
empower the model with external knowledge called Open-Domain Trigger Knowledge, defined as a prior that specifies which words can trigger events without subject to pre-defined event types and the domain of texts.
Knowledge Collection: apply a light-weight pipeline, called Trigger From WordNet (TFW), to equipment unlabeled sentences with trigger knowledge from WordNet. $S^+ = TFW(S)$ we obtain a total of 733,848 annotated sentences from New York Times corpus in the first half of 2007. The total number of triggers is 2.65 million, with an average of 3.6 triggers per sentence.,
disambiguate word into WordNet sense: adopt IMS (Zhong and Ng, 2010) to disambiguate word into word sense in WordNet. obtain the input features by POS tagger and dependency parser in Stanford CoreNLP
determine whether a sense triggers an event: adopt the simple dictionary-lookup approach proposed in (Araki and Mitamura, 2018)
given the knowledge enhanced data as well as ED annotations, we train a teacher model for better performance
Feature Extraction: adopt the sequence output of the last layer of BERT as the hidden representation for each word in S and S+
$\begin{aligned} H &=B E R T(S) \\\\ H_{+} &=B E R T\left(S_{+}\right) \end{aligned}$
Event Prediction: adopt a full-connected layer to determine the event type Y for each word in sentence S. where $O_{ijc}$ represents the probability that the j-th word in Si belongs to the c-th event class. normalize O by the softmax function to obtain the conditional probability
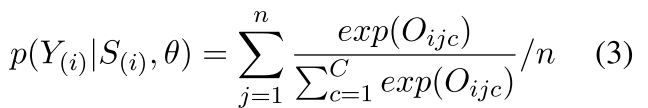
Given the labeled corpus $L = \\{S_i, Y_i \\}|_{i=1}^{N_L}$, optimization object is defined as
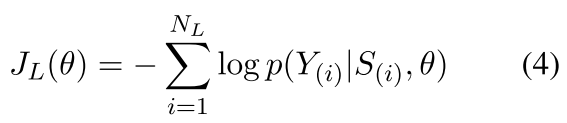
a student model is trained to mimic teacher’s outputs using data without knowledge enhancement, which conforms to the distribution during inference
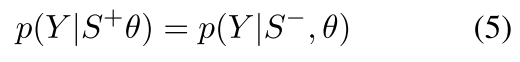
share the parameters of the teacher and student model
Knowledge-attending Sentences (S+): trigger $wi$ identified by open-domain trigger knowl edge, $S+ = {w1, w2, . . . ,B-TRI, wi, E-TRI, . . . , wn}$
- fine-tuning BERT with Mask LM on the annotation sentences S+ to address newly added symbols are lack of pre-trained embedding in BERT
Knowledge-absent Sentences (S−): 增加学生模型学习难度, disturb the input of student model by randomly masking out triggers, $S− = {w1, w2, . . . ,[MASK], . . . , wn}$
KL-divergence Loss: We move the added symbols to the end of the sentence to ensure strict alignment of words in S+ and S−, minimize the discrepancy between conditional probability p(Y|S−, θ) and p(Y|S+θ) with KL-divergence loss.
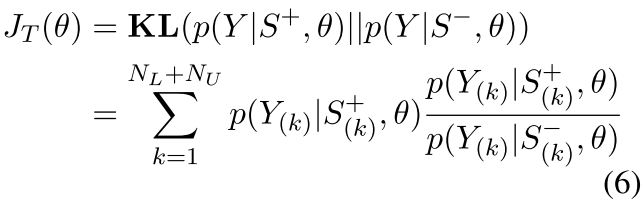
KL散度不对称, 这里使用无KG的预测来逼近有KG加成的预测的分布. 反过来则效果不好
Joint Training: supervised loss from labeled dataset and KL- divergence loss from unlabeled dataset
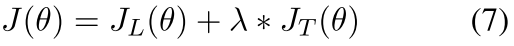
stop the gradient descent of teacher model when calculating JT to ensure that the learning is from teacher to student
Training Signal Annealing (TSA): Linearly release the ‘training signals’ of the labeled examples as training progresses 避免模型overfit少量的有标签数据而underfit 大量的无标签样本
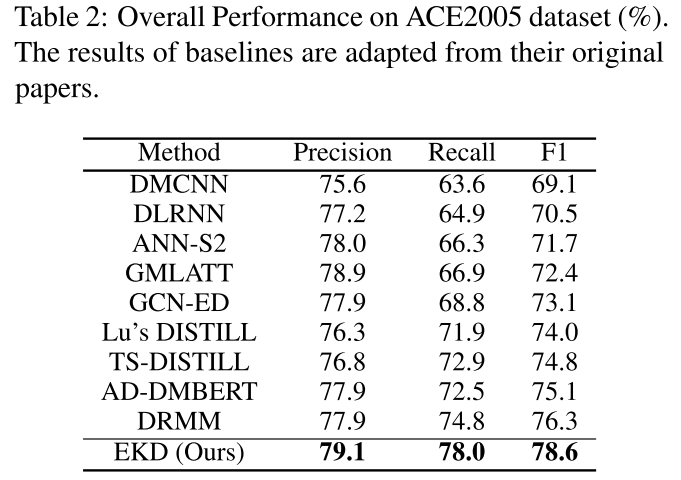
效果
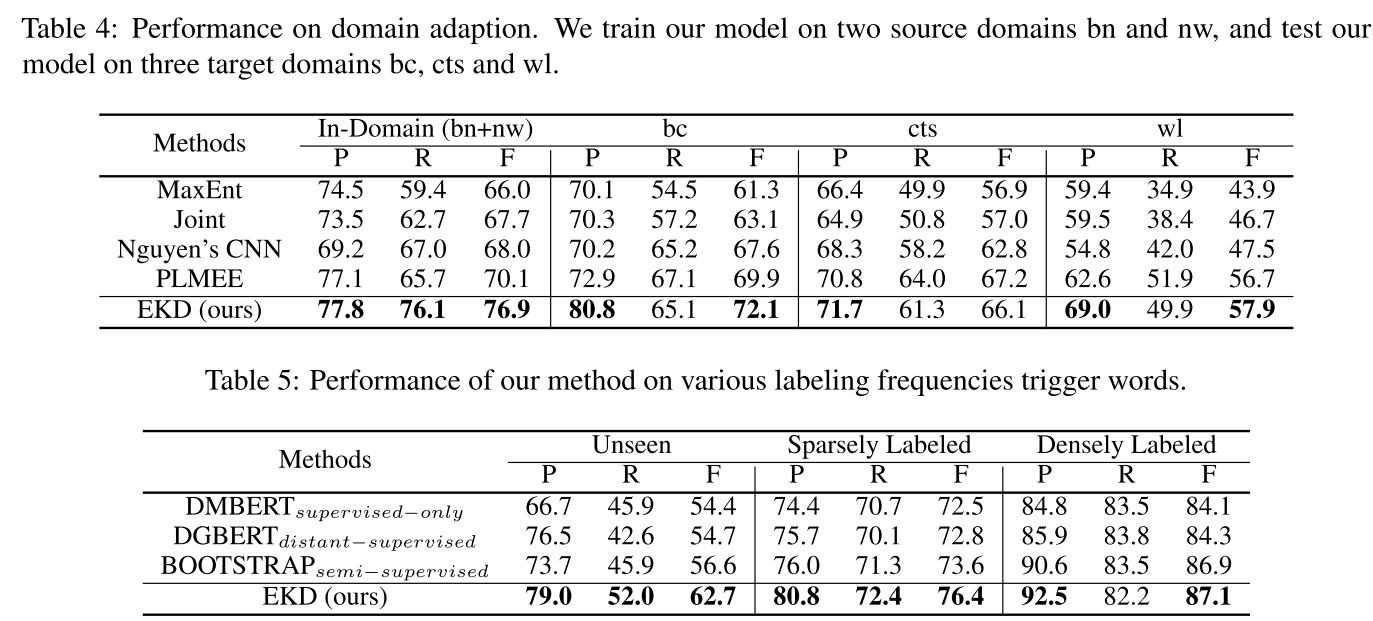
outperforms nine strong baselines, is especially effective for unseen/sparsely labeled trigger words.