2019, ACL
data: SemEval 2014, SemEval 2014 ABSA, SemEval 2015, SemEval 2016
task: ABSA
propose a span-based extract-then-classify framework, where multiple opinion targets are directly extracted from the sentence under the supervision of target span boundaries, and corresponding polarities are then classified using their span representations.
优点:
- 用指针网络选取target,避免了序列标注的搜索空间过大问题
- 用span边界+极性的标注方式,解决多极性的target问题
方法
Input:
sentence x =(x1,..., xn) with length n,
Target list T = {t1,..., tm}: each target ti is annotated with its start, end position, and its sentiment polarity
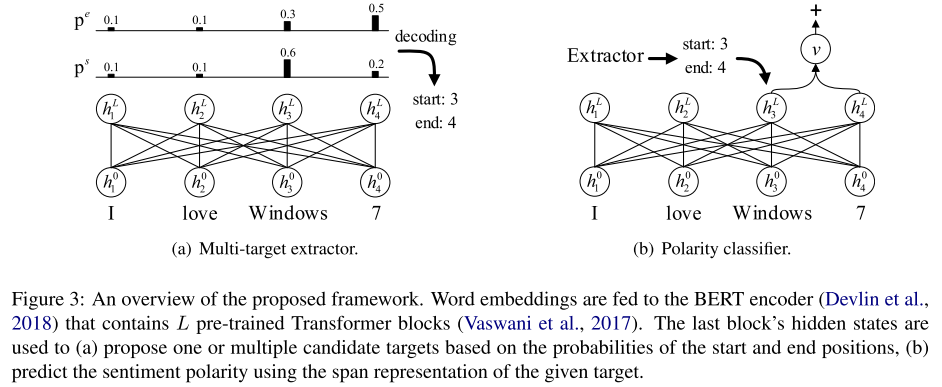
Multi-Target Extractor
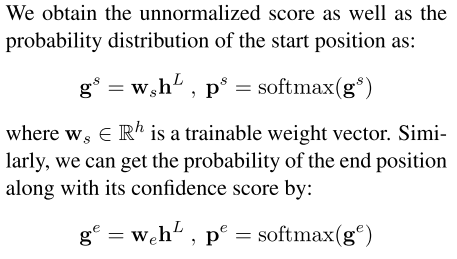

propose an heuristic multi-span decoding algorithm
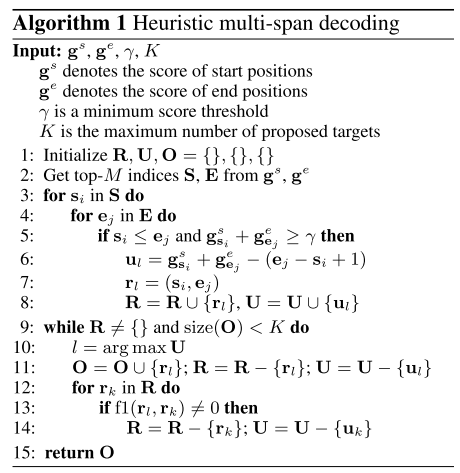
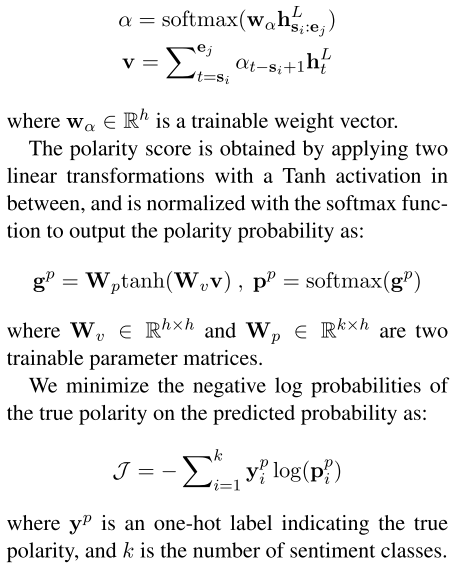
3.3 Polarity Classifier
given a target span r, we calculate a summarized vector v using the attention mechanism (Bahdanau et al., 2014) over tokens in its corresponding bound (si, ej)
3.4 Model Variants
Pipeline model:
- build a multi-target extractor where a BERT encoder is exclusively used.
- Then, a second backbone network is used to provide contextual sentence vectors for the polarity classifier.
- Two models are separately trained and combined as a pipeline during inference.
Joint model:
- Each sentence is fed into a shared BERT backbone network
- that finally branches into two sibling output layers: one for proposing multiple candidate targets and another for predicting the sentiment polarity over each extracted target.
Collapsed model: combine target span boundaries and sentiment polarities into one label space.
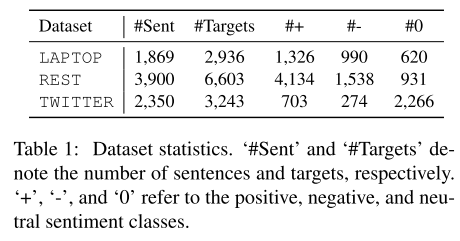
Data
SemEval 2014 ABSA
LAPTOP contains product reviews from the laptop domain in SemEval 2014 ABSA challenges
REST is the union set of the restaurant domain from SemEval 2014, 2015 and 2016
效果
Metrices We adopt the precision (P), recall (R), and F1 score