2020, EMNLP
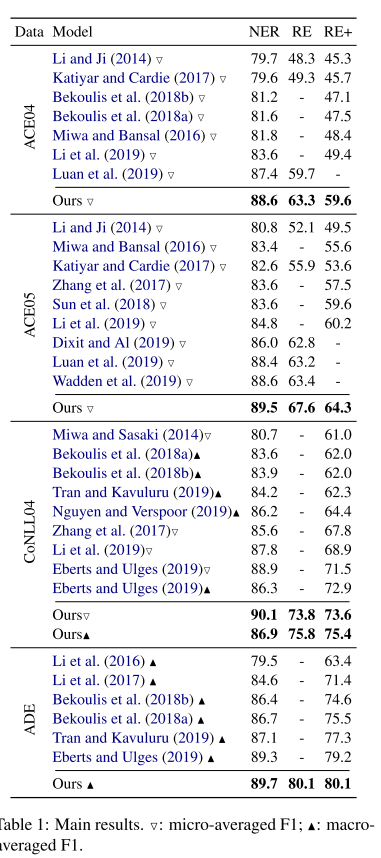
data: ACE 04, ACE 05, ADE, CoNLL04
links: https://github.com/LorrinWWW/two-are-better-than-one.
task: Entity and Relation Extraction
In this work, we propose the novel table-sequence encoders where two different encoders – a table encoder and a sequence encoder are designed to help each other in the representation learning process.
这篇ACL 2020文章认为, 之前的Joint learning方法侧重于learning a single encoder (usually learning representation in the form of a table) to capture information required for both tasks within the same space. We argue that it can be beneficial to design two distinct encoders to capture such two different types of information in the learning process.
- First, these methods typically suffer from feature confusion as they use a single representation for the two tasks – NER and RE
- Second, these methods underutilize the table structure as they usually convert it to a sequence and then use a sequence labeling approach to fill the table
方法
- we focus on learning two types of representations, namely sequence representations and table representations, for NER and RE respectively.
- we design a mechanism to allow them to interact with each other, in order to take advantage of the inherent association underlying the NER and RE tasks
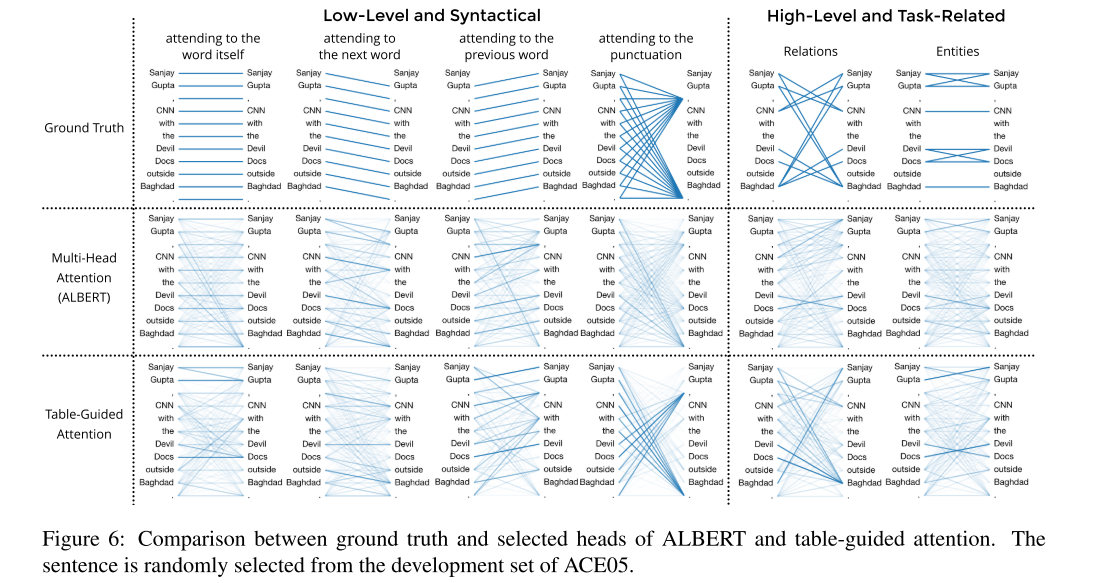
- use the attention weights of BERT for learning table representations.
Regard NER as a sequence labeling problem, where the gold entity tags yNER are in the standard BIO

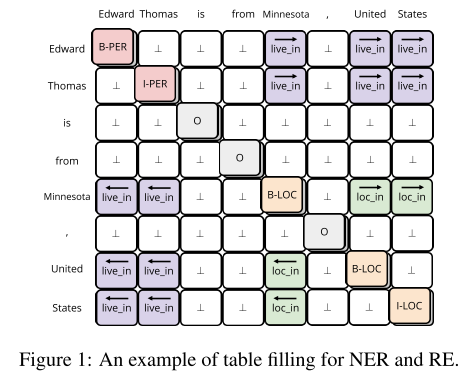
Model
The model consists of two types of interconnected encoders, a table encoder for table representation and a sequence encoder for sequence representation
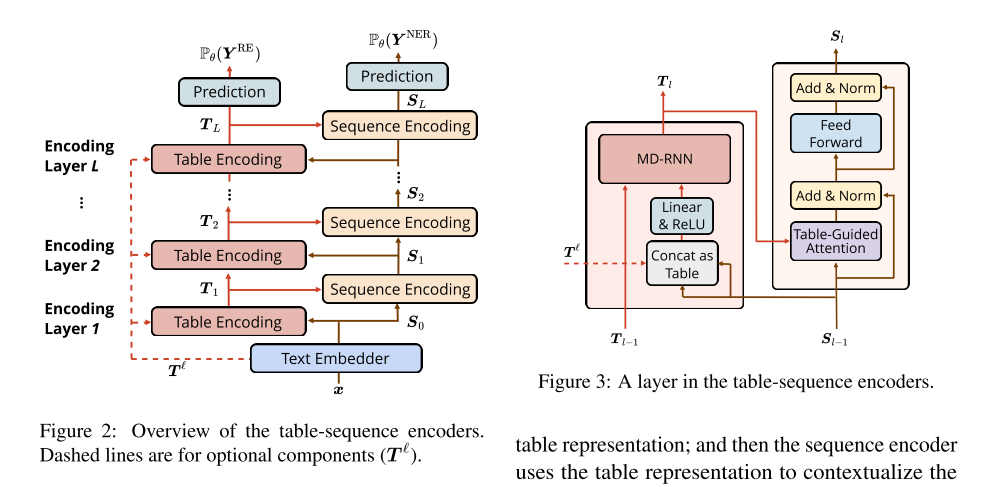
- In each layer, the table encoder uses the sequence representation to construct the table representation;
- and then the sequence encoder uses the table representation to contextualize the sequence representation
Table Encoder
first construct a non-contextualized table by concatenating every two vectors of the sequence representation followed by a fully-connected layer to halve the hidden size

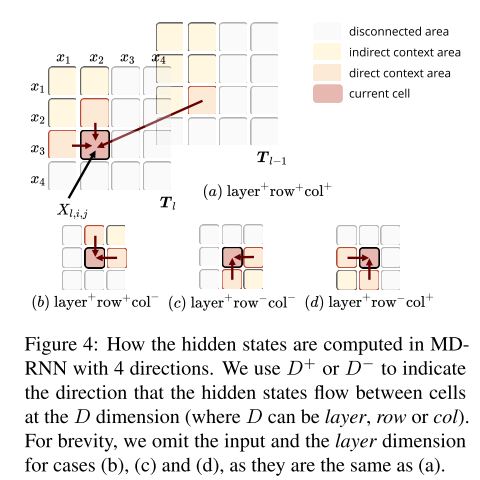
Next, we use the Multi-Dimensional Recurrent Neural Networks (MD-RNN) with Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), iteratively compute the hidden states of each cell to form the contextualized table representation, to access the context from four directions for modeling 2D data
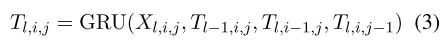
Empirically, we found the setting only considering cases (a) and (c) in Figure 4 achieves no worse performance than considering four cases altogether

Sequence Encoder
we replace the scaled dot- product attention with our proposed table-guided attention.
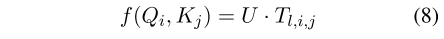
4.4 Exploit Pre-trained Attention Weights

效果